The curse of fashion and its cure
Guest post by Hafsa Hussain
On every item we own from our phones to the sheets on our beds, in small writing on the label it states, ‘Made in __’. This is most likely to originate from China or developing countries. But what is the story behind where our items are from, most importantly the clothes which we wear? Founder of Fashion Tech Lab, Miroslava Duma told the August 2017 Marie Claire, the first ever sustainable issue: “The fashion industry is all about storytelling and craftsmanship. Sustainability adds value because it makes that backstory even more impactful”. In recent years, consumers have been demanding more social and environmental information about the origin of the clothes they buy. This shows that more than ever, we are interested in our clothing, as the truth about the origin has been exploited in tabloids and documentaries, changing consumer attitudes.
Did you know that the fashion industry is one of the most polluting industries in the world after oil? With approximately 80 billion garments produced worldwide per year (Green Peace, 2016). This is due to the demand for new trends and styles increasing in recent years. According to the documentary, True Cost, rather than four seasons of collections per year, fast fashion has fabricated fifty-two seasons, creating new styles every week. Keeping in mind the lack of consideration for social and environmental consequences. Can the industry succeed by continuing with fast fashion and being ethical simultaneously?
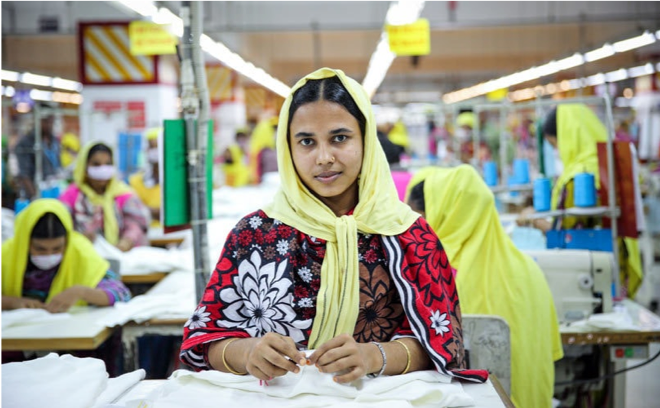

In the fashion industry momentarily, fast fashion has been speeding up trends and shortening seasons, whilst becoming old, dated and out of style. The average turnover period of designer brands from the catwalk to consumers is six months and has now been compressed from only a few weeks by companies such as Zara and H&M, whose profits are exceedingly high. Swift cycles make these fast fashion companies succeed: having fast designs, effective transportation and items prepared on hangers with price tags attached ready for the shop floor. As fast fashion replaces the luxury, authenticity and exclusivity with planned impulse, lasting for a limited time due to the poor-quality fabrics, manufacturers have gone out of fashion.

H&M, a mass fast fashion company, has focused on their ethical profiles for sales growth in the long-term. According to Corporate Knights magazine, H&M ranked 57th amongst the world’s most sustainable companies with an overall score of 65.10%; Whilst Kering ranked ten places above with a score of 66.80%. H&M launched a garment collecting service at their stores, recycling textiles to “give their garments a new life and helping to close the loop on fashion”, stating they have gathered more fabric in comparison to 250 million t-shirts. However, according to the Huffington Post, H&M continues to produce 600 million garments per year which is more than double the garments recycled and reused. As consumers, if we began re-using and recycling our items, rather than constantly buying new pieces and throwing others away, producers would have no choice but to change their strategies, and companies would consider evolving to a slow fashion movement

SOLUTIONS!
It’s time to change! There needs to be inventive strategies implemented to move from fast fashion to slow fashion, for the mass market sector, including the extension the product’s life cycle due to designs of clothes which are not molecular. For example, a coat which contains zips, buttons and trim can be recycled efficiently leaving just the fabric to be shredded back to its thread level, this new thread can become a new fabric and finally a new item of clothing. To achieve this, the jacket would need to have a mainframe hidden and attached in the coat’s fabric to hold the zips, button and trim altogether, and when the coat is at the end of its life cycle, the wireframe can be removed easily from the bone. Additionally, materials could be labelled with expected lifetimes including repair kits and services, provided by retailers, if the design development of the garments can be easily updated for the look or size.

Vintage clothing is commonly classified as clothing that is 20 years or older and if the garment survives more than 50 years it can be proudly called an antique. Vintage clothes are not only used pieces of garments, but it’s also part of history and adventure of thoughts of who wore them and their story to tell. Vintage clothing is a simple way to reduce, reuse and recycle clothes. During the manufacturing process, quality was important and key hence the fact they often last longer than most of the clothing today. But why has vintage fashion become popular recently, maybe because they can’t be replicated effortlessly or perhaps due to celebrities such as Kate Moss and Kim Kardashian having worn vintage on the red carpet? What people don’t realise is that fashion trends always come back around. Instead of throwing your ‘old’ clothes away, be patient, wait a couple years, fashion is not as new as you would think it is.
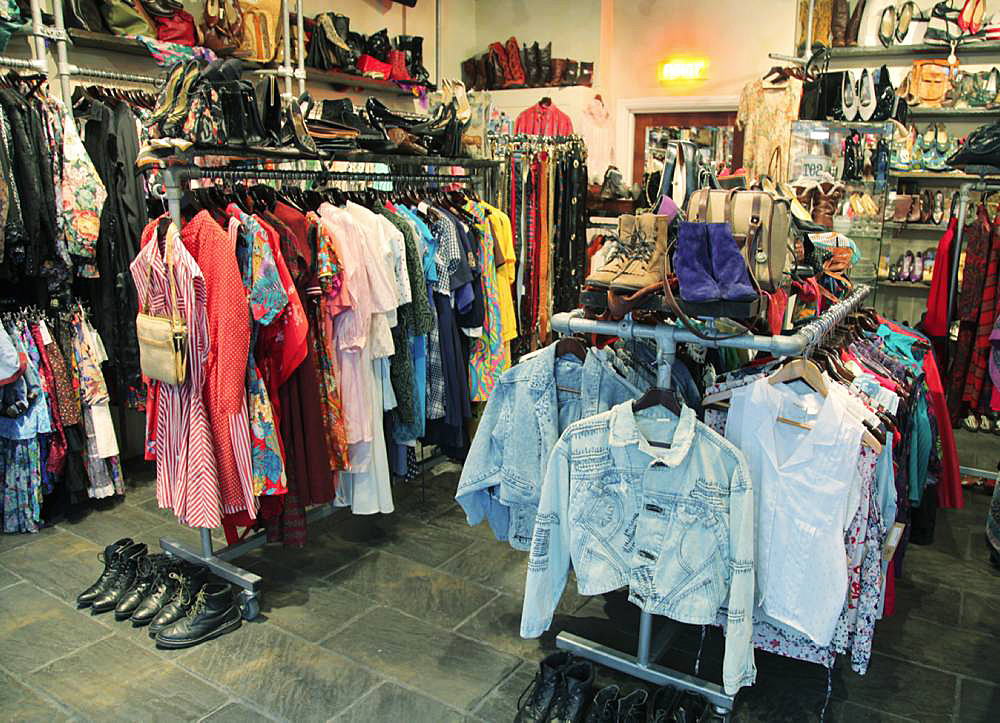

Recently we have seen a rise in 90s streetwear fashion on both our runways and on the streets. Big brands have dramatically increased their prices to offer ‘vintage’ pieces, but this could be saved if we as consumers actually visited vintage shops instead. Vintage can be advantageous in both ways, it allows you to differentiate yourself from the rest and it can also allow you to add to the current trends, so you look truly ahead of what the current runways have to offer.
Thank you!
Hafsa x